* ✨ Support token-based authentication for template addons
This change enables template type addons to work with both CSR-based
and token-based authentication through dynamic subject binding.
Changes:
- Modified createPermissionBinding() to extract dynamic subjects from
addon.Status.Registrations instead of using hardcoded groups
- Added buildSubjectsFromRegistration() helper to extract user/groups
from registration status
- Returns SubjectNotReadyError when subjects not ready (enables retry)
- Removed clusterAddonGroup() function (no longer needed)
- Updated addon-framework dependency to v1.2.0 for SubjectNotReadyError
- Added comprehensive tests for buildSubjectsFromRegistration
- Updated test helpers to include registration status with proper subjects
The implementation now supports:
- CSR-based authentication (existing)
- Token-based authentication (new)
- Any future authentication method that populates Status.Registrations
Related: 14af2a2eeb/enhancements/sig-architecture/167-token-based-addon-registration/README.md
🤖 Generated with Claude Code
https://claude.com/claude-code
Co-Authored-By: Claude Sonnet 4.5 <noreply@anthropic.com>
Signed-off-by: zhujian <jiazhu@redhat.com>
* test: add unit test for system:authenticated group filtering
Add a test case to verify that buildSubjectsFromRegistration correctly
filters out the system:authenticated group from the list of groups when
building RBAC subjects. This covers the filtering logic in
registration.go lines 560-562.
Also update the expected groups in TestTemplateCSRConfigurationsFunc
to match the implementation that includes both cluster-specific and
addon-wide groups for token-based authentication.
Signed-off-by: Claude <noreply@anthropic.com>
Signed-off-by: zhujian <jiazhu@redhat.com>
* feat: add addon-wide group and filter system:authenticated
Add support for addon-wide group in defaultGroups() to support
token-based authentication for template addons. This adds the
system:open-cluster-management:addon:{addonName} group in addition
to the cluster-specific group.
Also add filtering logic in buildSubjectsFromRegistration() to
exclude the system:authenticated group from RBAC subjects, as this
is a special Kubernetes group automatically added to all authenticated
users and should not be explicitly included in RoleBindings.
Signed-off-by: Claude <noreply@anthropic.com>
Signed-off-by: zhujian <jiazhu@redhat.com>
* refactor: implement custom CSR approver with flexible org validation
Replace addon-framework's DefaultCSRApprover with a custom implementation
that supports both legacy and new CSR organization structures.
Key changes:
- Implement defaultCSRApprover function that accepts 2 or 3 organization units
- 3 orgs: legacy behavior including system:authenticated group in CSRs
- 2 orgs: new behavior where system:authenticated is filtered out
- Add support for gRPC-based CSR requests by checking CSRUsernameAnnotation
- Validate all required default addon groups are present in CSR
- Add necessary imports: k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/util/sets and operatorapiv1
This enables backward compatibility while supporting the new token-based
authentication flow where system:authenticated is excluded from CSR orgs
but included in registration configs.
🤖 Generated with [Claude Code](https://claude.com/claude-code)
Co-Authored-By: Claude Sonnet 4.5 <noreply@anthropic.com>
Signed-off-by: zhujian <jiazhu@redhat.com>
* refactor: use addon-framework's updated KubeClientSignerConfigurations
Remove custom implementations and use addon-framework's native functions
which now include system:authenticated group by default.
Changes:
- Remove custom kubeClientSignerConfigurations function
- Remove custom defaultGroups function
- Remove custom defaultCSRApprover function
- Use agent.KubeClientSignerConfigurations from addon-framework
- Use utils.DefaultCSRApprover from addon-framework
- Remove unused imports: k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/util/sets and operatorapiv1
The addon-framework has been updated to include system:authenticated in
DefaultGroups(), eliminating the need for custom implementations.
🤖 Generated with [Claude Code](https://claude.com/claude-code)
Co-Authored-By: Claude Sonnet 4.5 <noreply@anthropic.com>
Signed-off-by: zhujian <jiazhu@redhat.com>
---------
Signed-off-by: zhujian <jiazhu@redhat.com>
Signed-off-by: Claude <noreply@anthropic.com>
Co-authored-by: Claude Sonnet 4.5 <noreply@anthropic.com>
Open Cluster Management (OCM) is a Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF) sandbox project focused on multicluster and multicloud scenarios for Kubernetes applications. At its core, OCM exists to make running, managing, and utilizing heterogeneous, multicluster environments simpler.
Project Goals and Objectives
We believe that no one runs just one cluster, and making multicluster management as easy as possible encourages community growth across all projects, empowering our users and their customers. Our core goal is to "multicluster everything."
OCM provides a flexible, extensible, and open model that allows any software project to easily understand how to run in a multicluster way. We align with and contribute to the SIG-Multicluster APIs for multicluster management while developing and sharing key concepts and components that make it easier and more accessible for any project, large or small, to "do multicluster."
Differentiation in the Cloud Native Landscape
Open Cluster Management differentiates itself in several key ways:
- Vendor Neutral: Avoid vendor lock-in by using APIs that are not tied to any cloud providers or proprietary platforms
- Standards-Based: We provide both a reference implementation of the APIs put forward by SIG-Multicluster as well as extended capabilities to accentuate them for numerous additional use cases
- Plug-and-Play Architecture: By standardizing on a single PlacementDecision API, any scheduler can publish its choices and any consumer can subscribe to them, eliminating friction and enabling true interoperability
- Extensible Framework: Our add-on structure allows projects to gain the benefits of simple, secure, and vendor-neutral multicloud management with minimal code changes
What OCM Does
OCM utilizes open APIs and an easy-to-use add-on structure to provide comprehensive multicluster management capabilities. We do this because we believe that managing multiple clusters should be simple and easy. With the variety of both free and proprietary cloud and on-premises offerings, it is important to help the community utilize these heterogeneous environments to their fullest potential.
Our architecture is modular and extensible, built to always model Kubernetes principles. We utilize open declarative APIs and build code with DevOps and automation. OCM runs on a hub-spoke model that can survive failure and recovery of components without interrupting workloads. It's containerized, vendor-neutral, and focuses on declarative management style aligned with GitOps principles.
Core Architecture
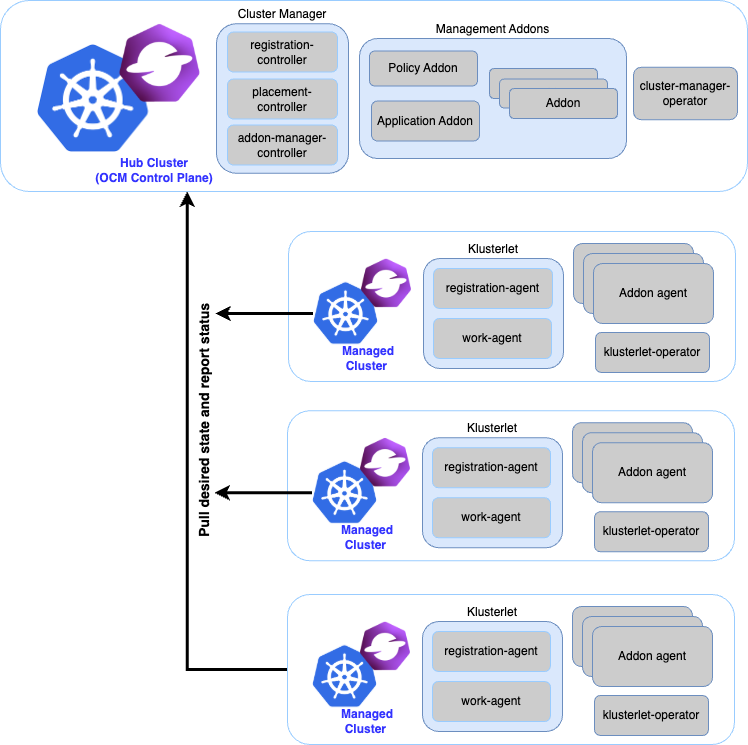
The OCM architecture uses a hub-spoke model where the hub centralizes control of all managed clusters. An agent, called the klusterlet, resides on each managed cluster to manage registration to the hub and run instructions from the hub.
Core Components
Cluster Inventory
Registration of multiple clusters to a hub cluster to place them for management. For comprehensive details on cluster inventory management, see the cluster inventory documentation. OCM implements a secure "double opt-in handshaking" protocol that requires explicit consent from both hub cluster administrators and managed cluster administrators to establish the connection.
The registration process creates an mTLS connection between the registration-agent on the managed cluster (Klusterlet) and the registration-controller on the hub (Cluster Manager). Once registered, each managed cluster is assigned a dedicated namespace on the hub for isolation and security. The registration-controller continuously monitors cluster health and manages cluster lifecycle operations including certificate rotation and permission management.
Work Distribution
The ManifestWork API enables resources to be applied to managed clusters from a hub cluster. ManifestWork acts as a wrapper containing Kubernetes resource manifests that need to be distributed and applied to specific managed clusters.
The work-agent running on each managed cluster actively pulls ManifestWork resources from its dedicated namespace on the hub and applies them locally. This pull-based approach ensures scalability and eliminates the need to store managed cluster credentials on the hub. The API supports sophisticated features including update strategies, conflict resolution, resource ordering, and status feedback to provide comprehensive resource distribution capabilities.
Content Placement
Dynamic placement of content and behavior across multiple clusters. The Placement API is a sophisticated scheduler for multicluster environments that operates on a Hub-Spoke model and is deeply integrated with the Work API.
The Placement API allows administrators to use vendor-neutral selectors to dynamically choose clusters based on labels, resource capacity, or custom criteria. The PlacementDecision resource provides a list of selected clusters that can be consumed by any scheduler or controller.
Add-on Framework
OCM Add-ons provide a clear framework that allows developers to easily add their software to OCM and make it multicluster aware. Add-ons are simple to write and are fully documented and maintained according to specifications in the addon-framework repository.
The framework handles the complex aspects of multicluster deployment including registration, lifecycle management, configuration distribution, and status reporting. Add-ons are used by multiple projects such as Argo, Submariner, KubeVela, and more. They are also used extensively for internal components of OCM, ensuring the framework is actively developed and maintained. With add-ons, any project can plug into OCM with minimal code and almost instantaneously become multicluster aware.
Built-in Extensions
These optional but valuable capabilities extend OCM's core functionality for specific use cases.
Cluster Lifecycle Management
OCM integrates seamlessly with Cluster API to provide comprehensive cluster lifecycle management. Cluster API is a Kubernetes sub-project focused on providing declarative APIs and tooling to simplify provisioning, upgrading, and operating multiple Kubernetes clusters.
The integration allows OCM to work alongside Cluster API management planes, where clusters provisioned through Cluster API can be automatically registered with OCM for multicluster management. OCM's hub cluster can run in the same cluster as the Cluster API management plane, enabling seamless workflows from cluster creation to workload deployment and policy enforcement. See the Cluster API integration guide for detailed setup instructions.
Application Lifecycle Management
Leverage the Argo CD add-on for OCM to enable decentralized, pull-based application deployment to managed clusters. The OCM Argo CD add-on uses a hub-spoke architecture to deliver Argo CD Applications from the OCM hub cluster to registered managed clusters.
Unlike traditional push-based deployment models, this pull mechanism provides several advantages:
- Scalability: Hub-spoke pattern offers better scalability
- Security: Cluster credentials don't have to be stored in a centralized environment
- Resilience: Reduces the impact of a single point of centralized failure
See Argo CD OCM add-on for details on installing the add-on and deploying applications across multiple clusters.
Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC)
Use prebuilt security and configuration controllers to enforce policies on Kubernetes configuration across your clusters. Policy controllers allow the declarative expression of desired conditions that can be audited or enforced against a set of managed clusters.
Related repositories:
Cloud Native Use Cases
Everything OCM does is Cloud Native by definition. Our comprehensive User Scenarios section provides detailed examples of how OCM enables various multicluster and multicloud use cases.
Getting Started
You can use the clusteradm CLI to bootstrap a control plane for multicluster management. To set up a multicluster environment with OCM enabled on your local machine, follow the instructions in setup dev environment.
For developers looking to contribute to OCM, see our comprehensive Development Guide which covers development environment setup, code standards, testing, and contribution workflows.
External Integrations
We constantly work with other open-source projects to make multicluster management easier:
- Argo CD (CNCF): OCM supplies Argo CD with ClusterDecision resources via Argo CD's Cluster Decision Resource Generator, enabling it to select target clusters for GitOps deployments
- Clusternet: (CNCF) Multicluster orchestration that can easily plug into OCM with clusternet addon
- KubeVela (CNCF): KubeVela develops an integration addon to work with OCM supporting application deployment across multiple clusters
- KubeStellar (CNCF): KubeStellar uses OCM as the backend of multicluster management
- Kueue (Kubernetes SIGs): OCM supplies Kueue with a streamlined MultiKueue setup process, automated generation of MultiKueue specific Kubeconfig, and enhanced multicluster scheduling capabilities
- Submariner: (CNCF) Provides multicluster networking connectivity with automated deployment and management
Documentation and Resources
For comprehensive information about OCM, visit our website with detailed sections on key concepts.
Community
Connect with the OCM community:
License
This project is licensed under the Apache License 2.0 - see the LICENSE file for details.