mirror of
https://github.com/jpetazzo/container.training.git
synced 2026-02-14 17:49:59 +00:00
➕️ Add chapter on Gateway API
This commit is contained in:
523
slides/k8s/gateway-api.md
Normal file
523
slides/k8s/gateway-api.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,523 @@
|
||||
# The Gateway API
|
||||
|
||||
- Over time, Kubernetes has introduced multiple ways to expose containers
|
||||
|
||||
- In the first versions of Kubernetes, we would use a `Service` of type `LoadBalancer`
|
||||
|
||||
- HTTP services often need extra features, though:
|
||||
|
||||
- content-based routing (route requests with URI, HTTP headers...)
|
||||
|
||||
- TLS termination
|
||||
|
||||
- middlewares (e.g. authentication)
|
||||
|
||||
- etc.
|
||||
|
||||
- This led to the introduction of the `Ingress` resource
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## History of Ingress
|
||||
|
||||
- Kubernetes 1.8 (September 2017) introduced `Ingress` (v1beta1)
|
||||
|
||||
- Kubernetes 1.19 (August 2020) graduated `Ingress` to GA (v1)
|
||||
|
||||
- Ingress supports:
|
||||
|
||||
- content-based routing with URI or HTTP `Host:` header
|
||||
|
||||
- TLS termination (with neat integration with e.g. cert-manager)
|
||||
|
||||
- Ingress doesn't support:
|
||||
|
||||
- content-based routing with other headers (e.g. cookies)
|
||||
|
||||
- middlewares
|
||||
|
||||
- traffic split for e.g. canary deployments
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Everyone needed something better
|
||||
|
||||
- Virtually *every* ingress controller added proprietary extensions:
|
||||
|
||||
- `nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/configuration-snippet` annotation
|
||||
|
||||
- Traefik has CRDs like `IngressRoute`, `TraefikService`, `Middleware`...
|
||||
|
||||
- HAProxy has CRDs like `Backend`, `TCP`...
|
||||
|
||||
- etc.
|
||||
|
||||
- Ingress was too specific to L7 (HTTP) traffic
|
||||
|
||||
- We needed a totally new set of APIs and resources!
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Gateway API in a nutshell
|
||||
|
||||
- Handle HTTP, GRPC, TCP, TLS, UDP routes
|
||||
|
||||
(note: as of October 2025, only HTTP and GRPC routes are in GA)
|
||||
|
||||
- Finer-grained permission model
|
||||
|
||||
(e.g. define which namespaces can use a specific "gateway"; more on that later)
|
||||
|
||||
- Standardize more "core" features than Ingress
|
||||
|
||||
(header-based routing, traffic weighing, rewrite requests and responses...)
|
||||
|
||||
- Pave the way for further extension thanks to different feature sets
|
||||
|
||||
(`Core` vs `Extended` vs `Implementation-specific`)
|
||||
|
||||
- Can also be used for service meshes
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
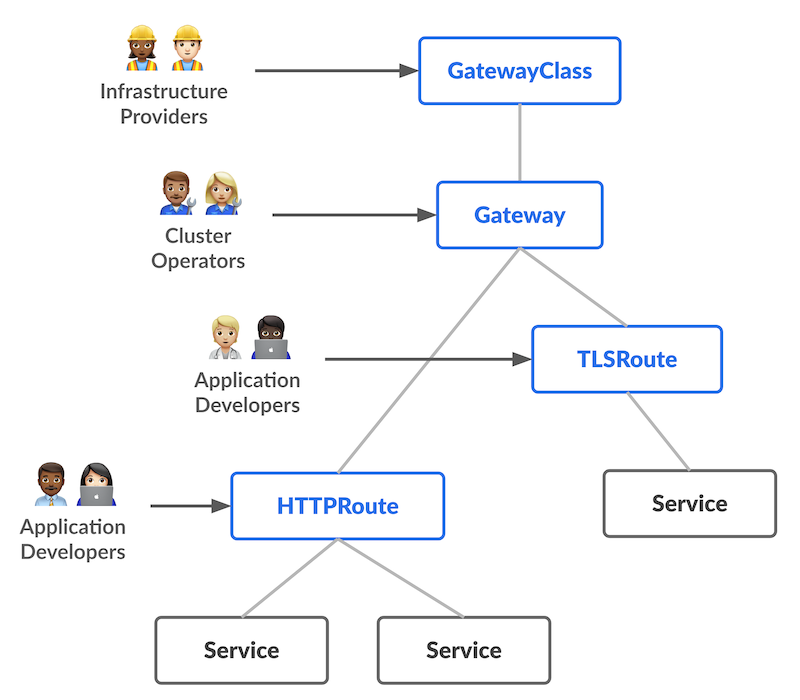
## Gateway API personas
|
||||
|
||||
- Ingress informally had two personas:
|
||||
|
||||
- cluster administrator (installs and manages the Ingress Controller)
|
||||
|
||||
- application developer (creates Ingress resources)
|
||||
|
||||
- Gateway [formally defines three personas][gateway-personas]:
|
||||
|
||||
- infrastructure provider
|
||||
<br/>
|
||||
(~network admin; potentially works within managed providers)
|
||||
|
||||
- cluster operator
|
||||
<br/>
|
||||
(~Kubernetes admin; potentially manages multiple clusters)
|
||||
|
||||
- application developer
|
||||
|
||||
[gateway-personas]: https://gateway-api.sigs.k8s.io/concepts/roles-and-personas/
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
class: pic
|
||||
|
||||
## Gateway API resources
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Gateway API resources
|
||||
|
||||
- `Service` = our good old Kubernetes service
|
||||
|
||||
- `HTTPRoute` = describes which requests should go to which `Service`
|
||||
|
||||
(similar to the `Ingress` resource)
|
||||
|
||||
- `Gateway` = how traffic enters the system
|
||||
|
||||
(could correspond to e.g. a `LoadBalancer` `Service`)
|
||||
|
||||
- `GatewayClass` = represents different types of `Gateways`
|
||||
|
||||
(many gateway controllers will offer only one)
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## `HTTPRoute` anatomy
|
||||
|
||||
- `spec.parentRefs` = where requests come from
|
||||
|
||||
- typically a single `Gateway`
|
||||
|
||||
- could be multiple `Gateway` resources
|
||||
|
||||
- can also be a `Service` (for cluster mesh uses)
|
||||
|
||||
- `spec.hostnames` = which hosts (HTTP `Host:` header) this applies to
|
||||
|
||||
- `spec.rules[].matches` = which requests this applies to (match paths, headers...)
|
||||
|
||||
- `spec.rules[].filters` = optional transformations (change headers, rewrite URI...)
|
||||
|
||||
- `spec.rules[].backendRefs` = where requests go to
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Minimal `HTTPRoute`
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
|
||||
kind: HTTPRoute
|
||||
metadata:
|
||||
name: xyz
|
||||
spec:
|
||||
parentRefs:
|
||||
- group: gateway.networking.k8s.io
|
||||
kind: Gateway
|
||||
name: my-gateway
|
||||
namespace: my-gateway-namespace
|
||||
hostnames: [ xyz.example.com ]
|
||||
rules:
|
||||
- backendRefs:
|
||||
- name: xyz
|
||||
port: 80
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Gateway API in action
|
||||
|
||||
- Let's deploy Traefik in Gateway API mode!
|
||||
|
||||
- We'll use the [official Helm chart for Traefik][traefik-chart]
|
||||
|
||||
- We'll need to set a few values
|
||||
|
||||
- `providers.kubernetesGateway.enabled=true`
|
||||
|
||||
*enable Gateway API provisioning*
|
||||
|
||||
- `gateway.listeners.web.namespacePolicy.from=All`
|
||||
|
||||
*allow `HTTPRoutes` in all namespaces to refer to the default `Gateway`*
|
||||
|
||||
[traefik-chart]: https://artifacthub.io/packages/helm/traefik/traefik
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## `LoadBalancer` vs `hostPort`
|
||||
|
||||
- If we're using a managed Kubernetes cluster, we'll use the default mode:
|
||||
|
||||
- Traefik runs with a `Deployment`
|
||||
|
||||
- Traefik `Service` has type `LoadBalancer`
|
||||
|
||||
- we connect to the `LoadBalancer` public IP address
|
||||
|
||||
- If we don't have a CCM (or `LoadBalancer` `Service`), we'll do things differently:
|
||||
|
||||
- Traefik runs with a `DaemonSet`
|
||||
|
||||
- Traefik `Service` has type `ClusterIP` (not strictly necessary but cleaner)
|
||||
|
||||
- we connect to any node's public IP address
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Installing Traefik (with `LoadBalancer`)
|
||||
|
||||
Install the Helm chart:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
helm upgrade --install --namespace traefik --create-namespace \
|
||||
--repo https://traefik.github.io/charts traefik traefik \
|
||||
--version 37.1.2 \
|
||||
--set providers.kubernetesGateway.enabled=true \
|
||||
--set gateway.listeners.web.namespacePolicy.from=All \
|
||||
#
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We'll connect by using the public IP address of the load balancer:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
kubectl get services --namespace traefik
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Installing Traefik (with `hostPort`)
|
||||
|
||||
Install the Helm chart:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
helm upgrade --install --namespace traefik --create-namespace \
|
||||
--repo https://traefik.github.io/charts traefik traefik \
|
||||
--version 37.1.2 \
|
||||
--set deployment.kind=DaemonSet \
|
||||
--set ports.web.hostPort=80 \
|
||||
--set ports.websecure.hostPort=443 \
|
||||
--set service.type=ClusterIP \
|
||||
--set providers.kubernetesGateway.enabled=true \
|
||||
--set gateway.listeners.web.namespacePolicy.from=All \
|
||||
#
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We'll connect by using the public IP address of any node of the cluster.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
class: extra-details
|
||||
|
||||
## Taints and tolerations
|
||||
|
||||
- By default, Traefik Pods will respect node taints
|
||||
|
||||
- If some nodes have taints (e.g. control plane nodes) we might need tolerations
|
||||
|
||||
(if we want to run Traefik on all nodes)
|
||||
|
||||
- Adding the corresponding tolerations is left as an exercise for the reader!
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
class: extra-details
|
||||
|
||||
## Rolling updates with `hostPort`
|
||||
|
||||
- It is not possible to have two pods on the same node using the same `hostPort`
|
||||
|
||||
- Therefore, it is important to pay attention to the `DaemonSet` rolling update parameters
|
||||
|
||||
- If `maxUnavailable` is non-zero:
|
||||
|
||||
- old pods will be shutdown first
|
||||
|
||||
- new pods will start without a problem
|
||||
|
||||
- there will be a short interruption of service
|
||||
|
||||
- If `maxSurge` is non-zero:
|
||||
|
||||
- new pods will be created but won't be able to start (since the `hostPort` is taken)
|
||||
|
||||
- old pods will remain running and the rolling update will not proceed
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Testing our Gateway controller
|
||||
|
||||
- Send a test request to Traefik
|
||||
|
||||
(e.g. with `curl http://<ipaddress>`)
|
||||
|
||||
- For now we should get a `404 not found`
|
||||
|
||||
(as there are no routes configured)
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## A basic HTTP route
|
||||
|
||||
- Create a basic HTTP container and expose it with a Service; e.g.:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
kubectl create deployment blue --image jpetazzo/color --port 80
|
||||
kubectl expose deployment blue
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## A basic HTTP route
|
||||
|
||||
- Create an `HTTPRoute` with the following YAML:
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
|
||||
kind: HTTPRoute
|
||||
metadata:
|
||||
name: blue
|
||||
spec:
|
||||
parentRefs:
|
||||
- group: gateway.networking.k8s.io
|
||||
kind: Gateway
|
||||
name: traefik-gateway
|
||||
namespace: traefik
|
||||
rules:
|
||||
- backendRefs:
|
||||
- name: blue
|
||||
port: 80
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- Our `curl` command should now show a response from the `blue` pod
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
class: extra-details
|
||||
|
||||
## Traefik dashboard
|
||||
|
||||
- By default, Traefik exposes a dashboard
|
||||
|
||||
(on a different port than the one used for "normal" traffic)
|
||||
|
||||
- To access it:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
kubectl port-forward --namespace traefik daemonset/traefik 1234:8080
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
(replace `daemonset` with `deployment` if necessary)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- Then connect to http://localhost:1234/dashboard/ (pay attention to the final `/`!)
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## `Core` vs `Extended` vs `Implementation-specific`
|
||||
|
||||
- All Gateway controllers must support `Core` features
|
||||
|
||||
- Some optional features are in the `Extended` set:
|
||||
|
||||
- they may or may not supported
|
||||
|
||||
- but at least, their specification is part of the API definition
|
||||
|
||||
- Gateway controllers can also have `Implementation-specific` features
|
||||
|
||||
(=proprietary extensions)
|
||||
|
||||
- In the following slides, we'll tag features with `Core` or `Extended`
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## `HTTPRoute.spec.rules[].matches`
|
||||
|
||||
Some fields are part of the `Core` set; some are part of the `Extended` set.
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
match:
|
||||
path: # Core
|
||||
value: /hello
|
||||
type: PathPrefix # default value; can also be "Exact"
|
||||
headers: # Core
|
||||
- name: x-custom-header
|
||||
value: foo
|
||||
queryparams: # Extended
|
||||
- type: Exact # can also have implementation-specific values, e.g. Regex
|
||||
name: product
|
||||
value: pizza
|
||||
method: GET # Extended
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## `HTTPRoute.spec.rules[].filters.*HeaderModifier`
|
||||
|
||||
`RequestHeaderModifier` is `Core`
|
||||
|
||||
`ResponseHeaderModifier` is `Extended`
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
type: RequestHeaderModifier # or ResponseHeaderModifier
|
||||
requestHeaderModifier: # or responseHeaderModifier
|
||||
set: # replace an existing header
|
||||
- name: x-my-header
|
||||
value: hello
|
||||
add: # appends to an existing header
|
||||
- name: x-my-header # (adding a comma if it's already set)
|
||||
value: hello
|
||||
remove:
|
||||
- x-my-header
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## `HTTPRoute.spec.rules[].filters.RequestRedirect`
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
type: RequestRedirect
|
||||
requestRedirect:
|
||||
scheme: https # http or https
|
||||
hostname: newxyz.example.com
|
||||
path: /new
|
||||
port: 8080
|
||||
statusCode: 302 # default=302; can be 301 302 303 307 308
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
All fields are optional. Empty fields mean "leave as is".
|
||||
|
||||
Note that while `RequestRedirect` is `Core`, some options are `Extended`!
|
||||
|
||||
(See the [API specification for details][http-request-redirect].)
|
||||
|
||||
[http-request-redirect]: https://gateway-api.sigs.k8s.io/reference/spec/#httprequestredirectfilter
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## `HTTPRoute.spec.rules[].filters.URLRewrite`
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
type: URLRewrite
|
||||
urlRewrite:
|
||||
hostname: newxyz.example.com
|
||||
path: /new
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`hostname` will rewrite the HTTP `Host:` header.
|
||||
|
||||
This is an `Extended` feature.
|
||||
|
||||
It conflicts with `HTTPRequestRedirect`.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## `HTTPRoute.spec.rules[].filters.RequestMirror`
|
||||
|
||||
This is an `Extended` feature. It sends a copy of all (or a fraction) of requests to another backend. Responses from the mirrored backend are ignored.
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
type: RequestMirror
|
||||
requestMirror:
|
||||
percent: 10
|
||||
fraction:
|
||||
numerator: 1
|
||||
denominator: 10
|
||||
backendRef:
|
||||
group: "" # default
|
||||
kind: Service # default
|
||||
name: log-some-requests
|
||||
namespace: my-observability-namespace # defaults to same namespace
|
||||
port: 80
|
||||
hostname: newxyz.example.com
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Specify `percent` or `fraction`, not both. If neither is specified, all requests get mirrored.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Other routes
|
||||
|
||||
- `GRPCRoute` can use GRPC services and methods to route requests
|
||||
|
||||
*this is useful if you're using GRPC; otherwise you can ignore it!*
|
||||
|
||||
- `TLSRoute` can use SNI header to route requests (without decrypting traffic)
|
||||
|
||||
*this is useful to host multiple TLS services on a single address with end-to-end encryption*
|
||||
|
||||
- `TCPRoute` can route TCP connections
|
||||
|
||||
*this is useful to colocate multiple protocols on the same address, e.g. HTTP+HTTPS+SSH*
|
||||
|
||||
- `UDPRoute` can route UDP packets
|
||||
|
||||
*ditto, e.g. for DNS/UDP, DNS/TCP, DNS/HTTPS*
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## `gateway.spec.listeners.allowedRoutes`
|
||||
|
||||
- With `Ingress`, any `Ingress` resource can "catch" traffic
|
||||
|
||||
- This could be a problem e.g. if a dev/staging environment accidentally (or maliciously) creates an `Ingress` with a production hostname
|
||||
|
||||
- Gateway API introduces guardrails
|
||||
|
||||
- A `Gateway` can indicate if it can be referred by routes:
|
||||
|
||||
- from all namespaces (like with `Ingress`)
|
||||
|
||||
- only from the same namespace
|
||||
|
||||
- only from specific namespaces matching a selector
|
||||
|
||||
- That's why we specified `gateway.listeners.web.namespacePolicy.from=All` when deploying Traefik
|
||||
|
||||
???
|
||||
|
||||
:EN:- The Gateway API
|
||||
:FR:- La Gateway API
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -64,8 +64,9 @@ content:
|
||||
- k8s/crd.md
|
||||
- #6
|
||||
- k8s/ingress-tls.md
|
||||
- k8s/ingress-advanced.md
|
||||
#- k8s/ingress-advanced.md
|
||||
#- k8s/ingress-canary.md
|
||||
- k8s/gateway-api.md
|
||||
- k8s/cert-manager.md
|
||||
- k8s/cainjector.md
|
||||
- k8s/eck.md
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -66,6 +66,7 @@ content:
|
||||
- k8s/rollout.md
|
||||
- k8s/healthchecks.md
|
||||
- k8s/ingress.md
|
||||
#- k8s/gateway-api.md
|
||||
#- k8s/volumes.md
|
||||
- k8s/configuration.md
|
||||
- k8s/secrets.md
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -86,6 +86,7 @@ content:
|
||||
- k8s/ingress-advanced.md
|
||||
#- k8s/ingress-canary.md
|
||||
- k8s/ingress-tls.md
|
||||
- k8s/gateway-api.md
|
||||
- k8s/cert-manager.md
|
||||
- k8s/cainjector.md
|
||||
- k8s/kustomize.md
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -84,6 +84,7 @@ content:
|
||||
#- k8s/ingress-advanced.md
|
||||
#- k8s/ingress-canary.md
|
||||
#- k8s/ingress-tls.md
|
||||
#- k8s/gateway-api.md
|
||||
- k8s/kustomize.md
|
||||
- k8s/helm-intro.md
|
||||
- k8s/helm-chart-format.md
|
||||
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user